How To Repair Septic System
Expert advice on septic tank issues, including how a septic tank works, and tips on septic tank pumping and replacing a failed septic tank.
Although sewers serve virtually metropolis and suburban homes, many homes in small towns and remote areas rely on septic tanks for on-site treatment of waste material water. In fact, according to the National Onsite Wastewater Recycling Association (NOWRA), nearly one-tertiary of the U.S. population rely on septic tanks.
For homes that utilize septic tanks, the septic system arguably may exist the well-nigh of import part of the inner workings—just inquire any homeowner who has had septic tank problems or failure.
The septic system should responsibly remove and dispose of all waste material from the home. As an organic machine, it breaks down wastes and, when working right, safely distributes the processed effluent into a drainfield on the property.
More than 1 trillion gallons of waste flow through septic systems each twelvemonth. Because that volume, the environment and public health rely on tanks operating correctly. Malfunctioning tanks can pollute ground and surface h2o with unsafe bacteria. Consequently, in developing countries, this type of contamination is responsible for outbreaks of disease, including hepatitis A, typhoid, and gastrointestinal illness.
As a result, proper maintenance is essential, and a full understanding of how your septic system works can put you mode alee of the game in avoiding septic tank bug.
Below you lot will find information on diverse septic tank and septic system bug, illustrated diagrams of how a septic arrangement works, and helpful communication on buying a new septic tank.
How a Septic Tank Works
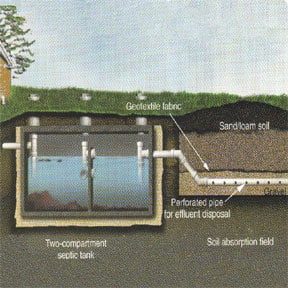
A septic tank separates and processes wastes. From the waste that flows into the tank, heavy solids settle to the bottom, forming a layer of sludge. Greases, oils, and lighter solids rise to the top, creating a layer of scum. The area between these two layers fills with liquid effluent that tin can flow through the outlet pipe to the drainfield organization.
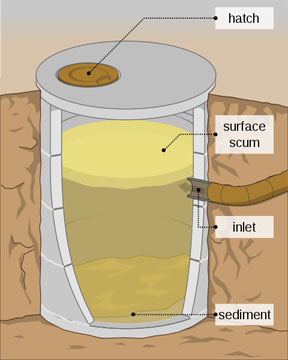
Inside the tank, anaerobic and facultative micro-organisms feed on the solids in the sludge and scum, breaking down their volume. This procedure creates gases—carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and others—that exit through the vent stack at the roof.
The proper size of a septic tank relates to the number of bedrooms in a house. The tank will typically shop solids for three to 12 years. The tank should be watertight—congenital then that groundwater cannot leak into the tank and seepage cannot leak out. If groundwater leaks into the tank, it volition raise the dissolved oxygen level in the tank, which will inhibit the biological handling, cause septic tank bug, and lead to early failure of the drainfield.
The Septic Drainfield
The drainfield should disperse a septic tank's effluent. Many bleed systems have a series of trenches that branch out from a distribution box. Some have a single, larger bed. Others have a seepage pit or a similar means of distributing tainted water dorsum into the ground (the right one for your home depends on local codes, conditions, and practices).
The absorption qualities of the soil dictate the drainfield's design. To gather information on how readily the soil will absorb water, a soils engineer or septic contractor conducts 'perk' (percolation) tests by digging holes in several places in the yard and filling them with water.
A conventional gravel-and-pipage drainfield begins with a level-bottom trench located from 1 to 3 feet beneath the ground, but at least ii anxiety above the groundwater table. A perforated drainpipe runs along the heart of the trench over 6 to 12 inches of gravel. A few more inches of gravel embrace it.
A silt barrier—a synthetic fabric—covers the gravel and pipage, rejecting silt and soil, and then soil backfills the trench. One time effluent reaches the drain system, the gravel and soil act equally a natural filter to strain and remove harmful bacteria, viruses, and other toxins so the water is clean past the time information technology reaches groundwater sources.
A newer type of drainfield system, fabricated by Infiltrator Systems, utilizes a serial of lightweight plastic chambers instead of pipe and gravel. These are easy to use and care for more h2o with greater efficiency.
The three-by-6 1/4-foot ribbed sections fit together and run along a three-human foot-wide trench. A special end plate caps the end of each run. You insert the inlet pipage into the main section, and backfill the trench.
Septic Tank Pumping & Care
Information technology pays to care for your tank (run across What Not to Flush, beneath) and invest in septic tank pumping periodically so the necessary bacteria don't die, shutting downwardly the biological automobile. When this happens, sludge builds upwards and flows into the drainfield, where it clogs up the system. Before you lot know it, you take a sewage fill-in, septic tank bug, and a major headache.

Because only a portion of the sludge and scum are broken downwardly (nearly twoscore percent), a septic tank must exist pumped periodically.
Otherwise, accumulated solids fill the tank and menstruation out into the drainfield, where they hinder the soil's ability to percolate.
Frequency of pumping depends on the size of the tank and the number of people using it. Nearly tanks require pumping every 3 to v years.
Don't wait too long. Y'all cannot pump the drainfield. If the drainfield is ruined because you pump the tank too infrequently, y'all may accept to install a new septic system at the cost of several thousand dollars. With proper care, a system should last well more than 20 years.
Where Is the Septic Tank?
You lot'll need to know where your septic tank is cached for inspection and pumping, and and so that you tin can avoid driving over the tank or leachfield with heavy equipment or doing other work that might damage the organization.
If you lot don't know where it is, you may be able to obtain records from your town or city hall. Otherwise, you tin hire a septic contractor, who may notice it with an electronic detector or by probing the soil with a long metal rod.
One time y'all've located your septic tank, make a map that shows its location and put the map where yous'll be able to find information technology in the future. In improver, mark the tank's location with a permanent stake or stone.
Tank Inspection
Have your tank inspected by a septic tank professional every three to 5 years—more frequently if your family uses a lot of h2o and a garbage disposer. You can reduce the strain on your septic system past using less water and staggering showers, clothes washing, bathing, and other heavy usage.
What Not to Flush
Be aware that what you flush or wash down the drain can damage the arrangement. Don't flush dyed or heavy toilet tissue or paper towels, feminine hygiene products, condoms, or disposable diapers.
Though some disinfectants, ammonia, and cleaners are not likely to significantly impairment a system, avert washing quantities of chemicals—peculiarly chlorine bleach—into the system.
Never cascade chemical bleed cleaners, solvents such as paint, motor oil, pesticides, poisons or chemicals into drainpipes. Minimize use of a garbage disposer and don't put fat, grease, or coffee grounds into it.
Beware that commercial affluent-down septic treatments may not work and, in fact, may damage information technology. They can promote the menses of sludge into drain lines, clogging the drainfield. Before using such a product, bank check with your health department to see if information technology has received state approval. Periodic inspection and pumping of your septic system are the best ways to ensure information technology operates for many years.
Septic Tank Issues or Failure
Accept some of these steps if your septic tank continually displays problems or is clearly in full failure mode.
To Minimize the Strain on Your Septic System
• Increase the size of the assimilation field. This will help if the original field was too small for the size of your family or if the soil does non permit water to percolate very well.
• Conserve water in your habitation on a long-term ground. The smaller the amount of water flowing through your system, the longer the system will last. For systems that perform marginally or leak nutrients into nearby lakes and streams, this is a good culling.
• If periodically saturated soils are a main cause of problems, consider installing perimeter drains. This organisation involves installing tile drains surreptitious at a specified distance effectually the absorption field to help lower water levels. This works in some just not all situations and requires the aid of a qualified contractor. Your system's location should also be evaluated past your local health department.
• Connect to a community sewage system, if ane is available. Although the long-term costs may seem high, the benefit of reduced worry is often worth the price.
• If septic system failures are mutual in your expanse, consider participating in the development of alternatives. There are systems designed for small communities and some rural areas that are generally much more cost-effective than large sewer systems.
To Deal with Septic Tank Failure
• First, telephone call your local health department. Health department staff members can expertly assess your state of affairs quickly and offering advice on how to cure the problem.
• Take your septic tank pumped. This volition assistance the problem temporarily. The empty tank tin can hold several days of waste material. Pumping won't solve a problem created by a clog located between the house and the septic tank. Neither will information technology help if very high groundwater levels are causing the problem.

• Conserve water. If your system has non failed completely, using less h2o can help lessen the problem for a short time. Water-saving devices and reduced consumption, especially in your bathroom, can have a significant upshot.
• Fence off the area. If liquid waste is seeping to the surface, prevent people and pets from getting in contact with the toxic effluent.
Tips for Ownership a New Septic Tank
In many cases, redesigning and replacing the organization in a new location is the only practical long term solution to chronic septic problems. For this type of work, hire a qualified septic contractor. Local health department normally require a let before construction can begin.
Equally explained above, a septic system is a self-independent h2o-recycling system. Located underground in the grand, a watertight tank receives and stores wastes from the house. Bacteria in the tank decompose the waste, sludge settles in the tank, and effluent flows into the basis through a bleed system. The effluent eventually filters back downwards to groundwater sources.

A septic system consists of a waste piping that is connected to the business firm's bleed-waste-vent system, a watertight septic tank, and a drainfield (or "leachfield") or other subsurface infiltration field such as a seepage pit or a leaching chamber.
Codes dictate the minimum distance a tank and drainfield may be located from the house or a well and the size and makeup of the tank and drainfield.
To forestall overloading the septic tank and drainfield, runoff from the roof and foundation drains and other 'clear' h2o is usually routed to a divide drain or seepage pit. Where codes permit, information technology'due south a good idea to route water from washing machines to such a pit, too.
Become a Pre-Screened Local Septic Arrangement Pro
Source: https://www.hometips.com/repair-fix/septic-tank-maintenance.html
Posted by: hawkinsausiout.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Repair Septic System"
Post a Comment